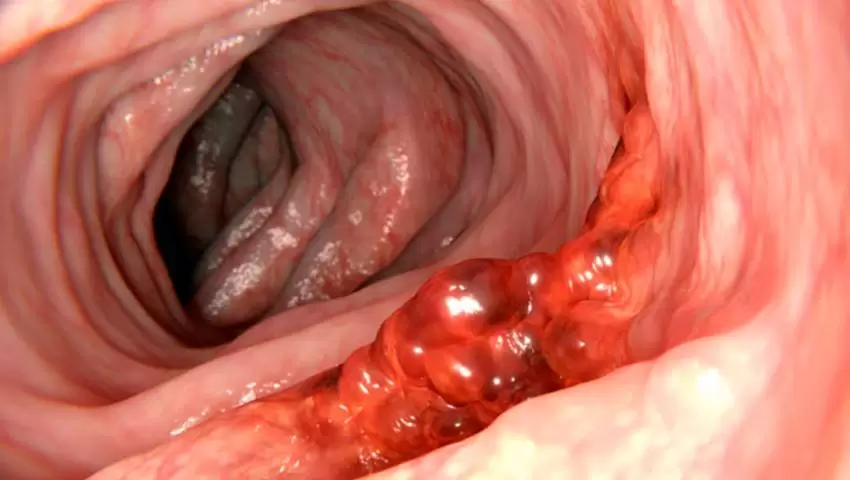
Rectal bleeding refers to the presence of blood in the stool or on toilet paper after a bowel movement. While it is often caused by minor issues such as hemorrhoids or anal fissures, it can sometimes signal more serious conditions, including colorectal cancer or inflammatory bowel disease.
Understanding the possible causes and knowing when to seek professional care is essential. Early evaluation by a specialist can guide accurate diagnosis and effective rectal bleeding treatment, ensuring the best outcomes and peace of mind.
Common, Less Serious Causes of Rectal Bleeding
Not all instances of rectal bleeding indicate a serious medical condition. In many cases, the bleeding is caused by minor and treatable issues that can be managed effectively with simple interventions. One of the most frequent causes is hemorrhoids, which are swollen blood vessels in the rectal or anal area. Hemorrhoids can be internal or external and often lead to bright red blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl.
Another common cause is anal fissures, small tears in the lining of the anus. These can occur after passing hard stools or straining during bowel movements, and typically cause sharp pain alongside bleeding. Minor trauma from constipation, straining, or even excessive wiping can also lead to small amounts of blood.
While these causes are generally not dangerous, it is still important to monitor symptoms. Persistent or recurrent bleeding should never be ignored, even if it seems minor. Seeking professional advice allows for proper evaluation and guidance on effective rectal bleeding treatment, including lifestyle modifications, medications, or simple procedures if needed.
Warning Signs That Require Immediate Attention
While minor causes of rectal bleeding are common, certain warning signs should prompt urgent medical evaluation:
- Persistent or heavy bleeding that continues over several bowel movements.
- Blood mixed with stool or dark, black, tarry stools, which may indicate bleeding higher in the digestive tract.
- Unexplained weight loss alongside rectal bleeding.
- Abdominal pain or cramping.
- Fatigue or weakness from potential blood loss.
- Noticeable changes in bowel habits, such as alternating constipation and diarrhea.
Even small amounts of blood accompanied by these symptoms can indicate more serious conditions, including colorectal cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, or vascular malformations.
Serious Conditions Associated with Rectal Bleeding
While many cases of rectal bleeding are minor, persistent or unusual bleeding can signal serious medical conditions. Understanding these possibilities helps patients recognize when professional evaluation is needed:
- Colorectal Cancer: One of the most concerning causes of rectal bleeding, especially in adults over 50. Blood may appear mixed with stool or cause changes in bowel habits. Early detection significantly improves outcomes.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Conditions such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis cause inflammation of the digestive tract, leading to bleeding, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and sometimes weight loss.
- Diverticulosis: Small pouches in the colon wall can occasionally bleed, leading to sudden, painless rectal bleeding.
- Vascular Malformations: Abnormal blood vessels in the digestive tract may cause intermittent bleeding, sometimes unnoticed until it becomes significant.
Even when bleeding seems mild, persistent or unexplained episodes should not be ignored.
Diagnostic Approach by a Colorectal Specialist
When rectal bleeding is persistent, unusual, or accompanied by other symptoms, a thorough evaluation by a colorectal specialist is essential. The diagnostic process typically includes:
1. Medical History and Physical Examination
The specialist will ask about the onset, frequency, and characteristics of the bleeding, as well as any associated symptoms such as pain, weight loss, or changes in bowel habits. A physical exam, including a digital rectal examination, helps identify obvious causes like hemorrhoids or anal fissures.
2. Colonoscopy or Sigmoidoscopy
These procedures allow direct visualization of the rectum and colon. They can identify sources of bleeding, inflammation, polyps, or tumors. Biopsies may also be taken during the procedure for further analysis.
3. Stool Tests and Blood Tests
Stool tests can detect hidden blood, infections, or inflammation. Blood tests help evaluate anemia or other underlying conditions.
4. Imaging Studies
In some cases, CT scans or MRI may be recommended to assess areas not visible with endoscopy, particularly if vascular malformations or deep-seated tumors are suspected.
Treatment Options (Depending on the Cause)
The treatment for rectal bleeding depends on the underlying condition. A colorectal specialist will recommend options tailored to each patient:
1. Minor Causes (such as Hemorrhoids or Anal Fissures)
- Lifestyle Modifications: Increase fiber intake, drink more water, and maintain regular bowel habits.
- Medications: Topical creams, ointments, or suppositories to reduce inflammation and discomfort.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Rubber band ligation or cauterization for persistent hemorrhoids.
2. Serious Conditions (such as Colon Cancer, IBD, or Diverticulosis)
- Surgical Interventions: Removal of tumors, polyps, or affected bowel segments.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, or targeted therapies for IBD.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regular colonoscopies and follow-ups to track progress and prevent recurrence.
3. Supportive Measures
- Pain Management: Analgesics or local treatments to relieve discomfort.
- Nutritional Guidance: Diet adjustments to reduce irritation and support bowel health.
Tailoring treatment to the specific cause ensures optimal outcomes and helps prevent future episodes of rectal bleeding.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Tips
Preventing rectal bleeding often starts with simple lifestyle adjustments. Eating a high-fiber diet that includes fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with staying well-hydrated, helps maintain smooth bowel movements and reduces strain. Avoiding prolonged straining during bowel movements and practicing proper toilet habits further supports rectal health.
Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight also contribute to overall digestive wellness. For individuals at higher risk, such as those over 50 or with a family history of colorectal conditions, routine screenings and check-ups are essential. Early detection and proactive care can lower the risk of serious complications and promote long-term bowel health.
Summary
While not all rectal bleeding is serious, persistent or unusual bleeding should never be ignored. Early evaluation by a colorectal specialist can help identify the underlying cause, ensure timely treatment, and provide peace of mind. Schedule a consultation with our colorectal surgeon in Singapore. Visit our clinic at:
Colonoscopy Doctor – Dr Aaron Poh | Colorectal Surgeon Singapore
3 Mount Elizabeth, #14-06a, Singapore 228510
Phone: +65 8875 0080