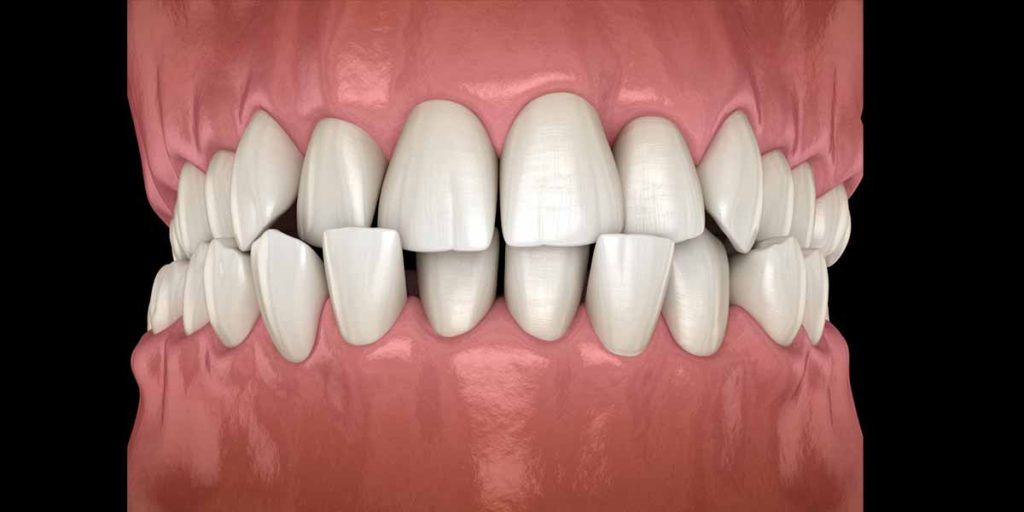
When we think about dental issues, crooked teeth or cavities often come to mind first. However, one condition that frequently goes unnoticed but can have significant effects on oral and overall health is a crossbite. A crossbite occurs when the upper and lower teeth do not align properly, causing some teeth to sit inside or outside their intended position when biting down. While this might seem like a minor issue, crossbites can lead to a range of problems, from jaw pain to speech difficulties.
In this blog, we’ll explore what causes crossbites, the impact they can have, and the treatment options available to correct them.
What Causes a Crossbite?
Crossbites can develop for several reasons, including genetics, habits, and developmental issues. Some common causes include:
- Genetics – A child may inherit jaw and tooth misalignment from parents. If one or both parents have a crossbite, there’s a higher chance their child will develop one as well.
- Delayed Baby Tooth Loss – If baby teeth do not fall out on time, they can prevent permanent teeth from emerging properly, leading to misalignment.
- Thumb Sucking & Pacifier Use – Prolonged thumb sucking or pacifier use beyond the toddler years can shape the palate abnormally, resulting in a crossbite.
- Mouth Breathing – Habitual mouth breathing due to nasal congestion or other issues can affect jaw development, contributing to crossbites.
Understanding the cause of a crossbite is important, as it can influence the treatment approach needed to correct the condition.
The Effects of a Crossbite
A crossbite might seem like a simple cosmetic issue, but it can have serious consequences for oral health and overall well-being. Some of the key effects include:
1. Tooth Wear and Damage
When teeth do not align properly, excessive pressure is placed on certain teeth, leading to uneven wear, enamel erosion, and even chipping or fractures. Over time, this can weaken the teeth and make them more susceptible to decay and sensitivity.
2. Jaw Pain and TMJ Disorders
A misaligned bite can put strain on the jaw joints, known as the temporomandibular joints (TMJ). This can result in symptoms like jaw pain, clicking sounds, headaches, and difficulty opening or closing the mouth. Long-term TMJ issues can lead to chronic discomfort and even impact daily activities like eating and speaking.
3. Gum Recession and Periodontal Problems
Misaligned teeth from a crossbite can create uneven pressure on the gums, leading to gum recession and an increased risk of gum disease. As the gums recede, they expose the roots of the teeth, making them more vulnerable to decay and sensitivity.
4. Facial Asymmetry and Growth Issues
In children, untreated crossbites can interfere with normal jaw development. Over time, this can cause facial asymmetry, making one side of the face appear more developed than the other. Early intervention can help guide proper jaw growth and prevent long-term issues.
5. Speech Difficulties
The positioning of the teeth plays a significant role in speech production. A crossbite can lead to speech impediments, such as lisping or difficulty pronouncing certain words. This can impact a child’s confidence and communication skills as they grow.
6. Chewing and Digestion Problems
Proper chewing is essential for digestion. A crossbite can make it difficult to chew food thoroughly, leading to digestive issues or discomfort after eating.
How is a Crossbite Treated?
The good news is that crossbites can be treated effectively with early intervention and the right dental care. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the crossbite and the patient’s age. Here are some common approaches:
1. Braces and Clear Aligners
Traditional braces, clear aligners (such as Invisalign), and bonding teeth braces are commonly used to gradually align teeth into their proper position. Braces are particularly effective for more severe crossbite cases, while clear aligners are a popular option for mild to moderate misalignments. Bonding may also be used in some instances to reshape or correct the positioning of specific teeth.
2. Palatal Expanders
For children with developing jaws, a palatal expander can be used to widen the upper jaw. This device helps correct crossbites before they become more severe, ensuring proper alignment as permanent teeth emerge.
3. Tooth Reshaping or Dental Bonding
In cases where a single tooth is misaligned, dentists may use tooth reshaping or bonding to adjust its position. This is a minimally invasive option but is only suitable for mild crossbites.
4. Orthognathic Surgery
For severe crossbites caused by skeletal misalignment, jaw surgery may be necessary. This is typically reserved for adults whose jaws have fully developed and cannot be corrected with orthodontic treatment alone.
The Importance of Early Intervention
While crossbites can be treated at any age, early diagnosis and intervention lead to better outcomes and fewer complications. Children and teenagers benefit the most from treatment, as their jaws are still growing and more adaptable to correction.
If you suspect a crossbite in yourself or your child, visiting an orthodontist as soon as possible is crucial. A professional evaluation can determine the severity of the crossbite and the best course of action.
In Conclusion
Crossbites are more than just a dental misalignment – they can have far-reaching effects on oral health, jaw function, and overall well-being. From tooth wear and jaw pain to speech difficulties and facial asymmetry, the impact of a crossbite should not be ignored.
Fortunately, with modern orthodontic treatments, crossbites can be corrected effectively. Whether through braces, expanders, or other interventions, seeking treatment early can prevent long-term issues and improve both function and aesthetics.
If you or your child has a crossbite, don’t wait – schedule a consultation with a dental professional today to explore your treatment options and take the first step toward a healthier, more confident smile!